Sedimentary Geology, 47 (1986), 191-219
SYNTECTONIC SEDIMENTATION IN A MIDDLE TRIASSIC RIFT, NORTHERN APENNINES,
ITALY
I.P. MARTINI1, A. RAU2 and M. TONGIORGI3
1Department of Land Resource Science, University of Guelph, Guelph,
Ont. N1G 2W1 (Canada)
2Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Centro di Studio per la Geologia
Strutturale e Dinamica dell'Appennino, Pisa (Italy)
3Dipartamento di Scienze della Terra, Universito di Pisa, Pisa
(Italy)
¡¡
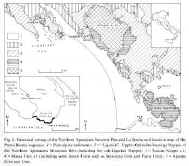 The anatomy of the sedimentary and volcanic fill of a Middle Triassic
continental rift at the western margin of the Tethys is illustrated by the study
of a 250 m thick sequence on the Tyrrhenian coasts of the Northern Apennines.
This sequence contains two cycles of sedimentation:
The anatomy of the sedimentary and volcanic fill of a Middle Triassic
continental rift at the western margin of the Tethys is illustrated by the study
of a 250 m thick sequence on the Tyrrhenian coasts of the Northern Apennines.
This sequence contains two cycles of sedimentation:
(a) The lower cycle
comprises a basal transgressive sequence from continental alluvial fans to
shallow marine carbonates, and an upper sequence that correspond to an
increasing tectonic activity (sub- marine syntectonic facies assemblage). The
lower part of the last assemblage is characterized by a thick (22 m), rapidly
deposited sequence of coarse carbonate breccias with minor calcareous sandy
turbidites. This is overlain by channelized red beds of submarine fans composed
of close interstratification and juxtaposition of carbonate breccias with red
clastic matrix, and red sandy quartz pebble conglomerates and silty sands.
Interbedded alkaline pillow lava record penecontemporaneous submarine eruptions.
The lavas are capped by thin red cherty (diaspri) crusts. The lower cycle of
sedimentation ends with a karstic surface on relatively deep marine carbonate
layers. This suggests a rapid emersion due to the arrest and reversal of the
downsinking of the initial ("aborted" or failed) rift.
(b) The upper cycle of
sedimentation starts with more mature fluvial red beds and changes upward into
shallow marine sands and carbonates. This upper cycle represents an early stage
of evolution of a new major rift. This second major rift led, in Jurassic times,
to the opening of an oceanic area between Europe and western Italy.