HST for Procurement
Specific Item Tax Status Guide:
HST For Purchasing
2.1 General Information for Purchasing
2.2 Exempt, Zero Rated, and Point of Sale Rebate Purchases
2.2.1 Exempt Purchases
2.2.2 Zero Rated Purchases
2.2.3 Point of Sale Rebates
2.3 Imported Purchases
2.4 Public Service Body Rebates
2.5 Input Tax Credits
2.6 Decision Tree
2.7 Procurement Card Purchases
2.8 Further Information
HST for Accounts Payable
2.9 General Information
2.9.1 Domestic Suppliers
2.9.2 Foreign Suppliers
2.10 Accounting for Purchases
2.11 Exempt, Zero Rated, and Point of Sale Rebate Purchases
2.12 Documentary Requirements
2.13 Rebates on Purchases
2.14 Input Tax Credits
2.14.1 Non Capital Expenses
2.14.2 Capital Expenses
2.15 Book Rebates
2.16 Construction - Physical Resources
2.17 Online Purchases
2.18 Insurance
2.19 Tax Included Purchases
2.20 Single vs. Multiple Supplies
2.21 Travel Expense Reimbursements
2.22 Projects Outside Ontario
2.23 Self Assessment requirements
2.24 Canadian Customs
2.25 T4ANRs
2.1 General Information (Purchasing)
Purchasing staff need to understand the tax status of various supplies in order to issue purchase orders that will match the invoice and to properly evaluate RFP responses. Tax is also important for budgeting in instances where the University cannot fully recover the tax it pays.
Almost all goods and services are HST taxable. Unlike the previous Ontario PST, it is the responsibility of the registered supplier to charge HST to the purchaser. If the wrong tax is applied, the vendor should be notified. The tax should not be self-assessed.
Generally, GST/HST applies to the value of the consideration for taxable supplies of goods or services made in Canada. While the consideration is usually expressed in money, the consideration, or part of the consideration, may be something other than money, such as property or a service. In such cases, the value of the consideration, or part of the consideration, is the fair market value of the property or service.
The word “supply” includes most forms of good and services. The scope of the GST/HST is not restricted to the provision of goods and services by way of sale but also includes other types of transactions, including leases and rentals, barter transactions, the granting or assignment of a right, or even an agreement not to do something.
The payment of money and the provision of an employee’s services to an employer are not supplies. However, certain actions carried out for no consideration may still cause GST to be exigible; for example, imports of services and intangibles by a Canadian branch from a foreign branch of the same person, or benefits provided to employees.
The standard rate of GST is 5 percent. Five Canadian provinces (Ontario, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, and Prince Edward Island) impose the Harmonized Sale Tax (HST). The rate of HST varies from 13 percent to 15 percent. The HST is a combination of a federal component (5 percent) and a provincial component (8 percent to 10 percent). In all material respects (tax base and mechanics) the HST system is essentially identical to the GST system. Ontario and Prince Edward Island have temporary recaptured input tax credit requirements of the provincial component of the HST on some expenditures.
HST is not charged on all Canadian Purchases. The supplier does not charge HST when:
- The goods and services are tax exempt
- The goods and services provided are zero rated
- The supplier or vendor is too small to be registered, despite supplying taxable goods and service. Small suppliers with annual sales of less than $30K do not have to register to charge tax. There is no requirement to self assess either.
2.2 Exempt, Zero Rated, and Point of Sale Rebate Purchases
Certain purchases made by the University are exempt from the HST (no HST is ever paid by the University).
There are two types of categories where the HST is not paid and are effectively considered to be tax exempt:
- With purchases that are considered to be tax exempt, your suppliers do not charge the HST.
- With purchases that are considered to be zero rated, the HST is charged to the University, but the rate of tax is 0%, not 13%. Again, no tax is paid.
You cannot claim rebates or ITCs on exempt or zero-rated purchases because you do not pay any tax.
2.2.1 Exempt Purchases
Almost all of the purchases that Guelph makes that are tax exempt are for services NOT goods. Approximately 33% of the services purchased by Guelph are tax-exempt.
Most of the categories of exemption are set out in the Tax Status Chart for Purchases [See Tax Status Chart for Purchases]. Please note that the chart is not exhaustive and there are special situations that it does not cover.
The top categories of exempt purchases that Guelph makes (in order of magnitude) are:
- Financial Services (such as banking or insurance)
- Services provided by other Universities or Hospitals
- Services provided by Charities and Non-Profits
- Grants and Subsidies (not considered to be subject to taxation)
- Municipal Services (public transit etc.)
- Residential Leases and Rentals
2.2.2 Zero Rated Purchases
If a purchase is zero rated, the supplier will charge tax at 0% (no tax). As such, being zero-rated is the same as being exempt from the purchaser’s perspective. The supplier on the other hand considers the sale to be taxable (at 0%) and can recover input tax credits on its own expenses.
Almost all purchases that are zero-rated are goods, not services.
Most of the categories of zero rated purchases are set out in the Tax Status Chart for Purchases [See Tax Status Chart for Purchases]. Please note that this list is not exhaustive and there are special situations that it does not cover.
The zero rated goods most commonly purchased by Guelph are:
- Most Agricultural Equipment and Supplies (tractors, seeds, grains, fertilizer etc.)
- Medical Devices & Prescription Drugs
- Basic Groceries (mainly purchased by Food Services in order to make food sales)
2.2.3 Point of Sale Rebates
If a purchase is eligible for a point of sale rebate, the vendor should not charge the provincial portion of the HST. In other words, Guelph should only be charged 5% GST (could also be referred to as the federal portion of HST).
Most point of sale rebates are set out in the Tax Status Chart for Purchases [See Tax Status Chart for Purchases].
2.3 Imported Purchases
Almost all goods that are imported by the university are taxable.
Most foreign suppliers are not registered by the CRA to collect and charge HST. Therefore, with imported goods, the 5% federal HST is automatically charged by Canada Customs when the goods cross the border into Canada. The purchaser must self assess the 8% provincial HST.
The exception to these rules are imported zero rated goods. The same goods that are zero rated when purchased from Canadian suppliers are also zero rated when the goods are imported.
Intangible property and services do not physically cross the border and therefore cannot be taxed by Canada Customs. If the vendor does not charge the tax, Guelph is required to self assess 13% HST in most cases.
Self assessed tax and tax charged by Canada Customs are eligible for the same rebates and input tax credits as tax charged by a vendor. If a purchase is to be used in commercial activities such that Guelph could recover all of the tax paid as an input tax credit (100% ITC), self-assessment is not required. Please refer to [section 2.23] for further details and examples
2.4 Public Service Body Rebates
The University may claim a rebate of the HST it pays when it purchases goods and services.
The reason for this special rebate is that, prior to the introduction of the GST, universities enjoyed many exemptions under the old Federal Sales Tax system. The federal government did not want universities to be harmed when the 5% GST was introduced. Similarly, the Ontario government did not want universities to bear a higher tax burden with the introduction of the 8% Provincial HST. There were many exemptions available for universities with the 8% PRST prior to the introduction of the Provincial HST.
The university claims a 67% rebate on the 5% federal portion of the HST (the GST).
The university claims a 78% rebate on the Provincial Portion of the HST (which replaced the PST).
Please refer to [section 2.13] for further details
When Guelph purchases goods that are eventually sold to consumers, a full Input Tax Credit (ITC) is claimed.
This is the same with sales made by private businesses. It is the final consumer that pays the HST. The ITC ensures that there is no embedded tax.
Unlike a rebate, the University claims a 100% ITC of the HST paid. If the items purchased are only partially use for resale, the ITC must be claimed on that part of the HST paid. The rebate may be applied on the remaining portion.
Please refer to [section 2.14] for further details
The following decision tree has been created to help you determine the tax status of a purchase:
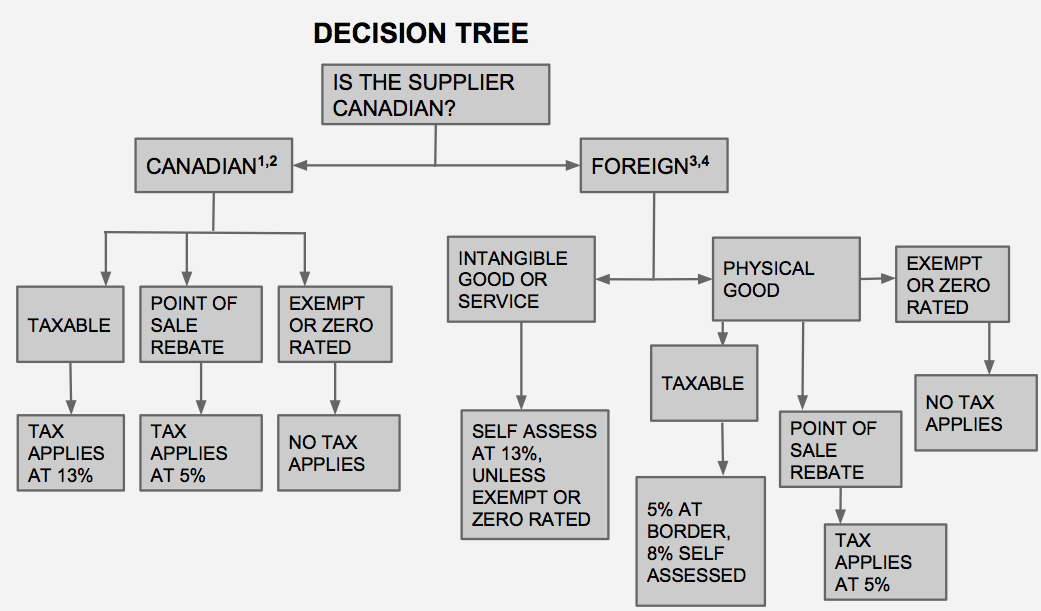
Footnotes:
- It is the supplier’s responsibility to charge tax correctly. If the wrong tax is applied, the vendor should be notified. The tax should not be self-assessed.
- Small suppliers with annual sales of less than $30K do not have to register to charge tax. There is no requirement to self assess the tax either.
- This applies to unregistered foreign suppliers.
- Self-assessment is not required if the supply is not considered to be consumed in Canada. Situations like this should be very rare and handled on a case-by-case basis.
Notes to accompany the decision tree:
The following website can be used to confirm that a GST/HST registration is valid. Any supplier that is registered for GST will also be registered for HST. There is no separate HST registration. http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/gsthstregistry/
Exempt and zero-rated are the same from a purchasing perspective. If a supply is exempt, no tax is applied. If a supply is zero rated, tax applies at 0%. A vendor can claim input tax credits with respect to zero rated supplies, but for the purchaser it makes no difference.
2.7 Procurement Card Purchases
Procurement cards (pcards) are credit cards used by departments for purchases of supplies and other low value items.
Pcard purchases are eligible for rebates and input tax credits just like any other purchase.
The self-assessment rules [see self assess section 3.15] apply to pcard purchases. To self assess means to calculate how much tax should be paid on the purchase of a good or service, and then to remit the tax. It is often required on foreign purchases.
The most common tax statuses that might apply to purchases are as follows:
| Tax Status | Canadian Vendor | Foreign Vendor |
|---|---|---|
| Taxable good for use in Guelph's exempt activities |
13% charged by vendor |
5% assessed at border, self-assess 8% |
| Taxable good for use in Guelph's commercial activities |
13% charged by vendor | 5% assessed at border, no self-assessment required |
| Taxable service or intangible for use in Guelph's exempt activities |
13% charged by vendor | self-assess 13% |
| Taxable service or intangible for use in Guelph's commercial activities |
13% charged by vendor |
no self-assessment required |
| Exempt | No tax | No Tax |
Please note that this table assumes that the place of supply is Ontario. In some cases, the place of supply may be another province. If a Canadian or foreign registered vendor charges tax based on place of supply in another province, self-assessment is required if the supply is to be consumed in Ontario.
2.9 General Information (Accounts Payable)
2.11 Exempt, Zero Rated, and Point of Sale Rebate Purchases
2.16 Construction - Physical Resources
2.20 Single vs. Multiple Supplies
2.21 Travel Expense Reimbursements
2.23 Self Assessment requirements
