What is quantitative proteomics?
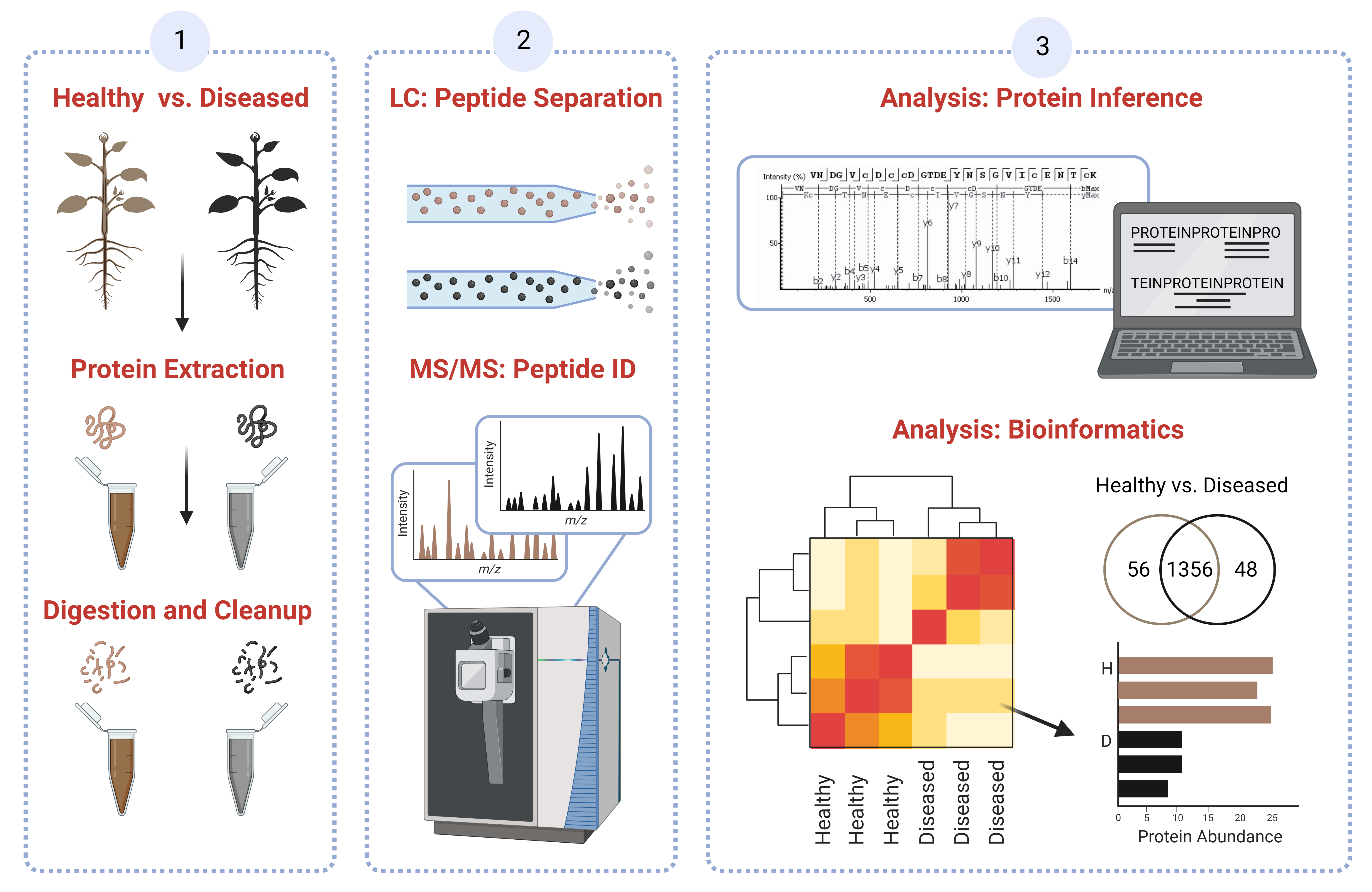
Quantitative proteomics uses liquid-chromatography (LC)-based separation combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry (MS) to identify proteins from biological samples then quantify relative changes in protein expression in two or more biological states.
How can you use quantitative proteomics?
LC-MS-based quantitative proteomics is a powerful analytical method that generates large and complex datasets that can be used to examine systematic changes in biological states, monitor specific pathways, or identify individual protein targets. The breadth of options can be difficult to navigate, and proper planning and sample preparation is key to success. Reach out to the Mass Spectrometry Facility (MSF) to learn how quantitative proteomics can benefit your research. The figure MS Quant Proteomics Decision tree below can help you navigate the options.
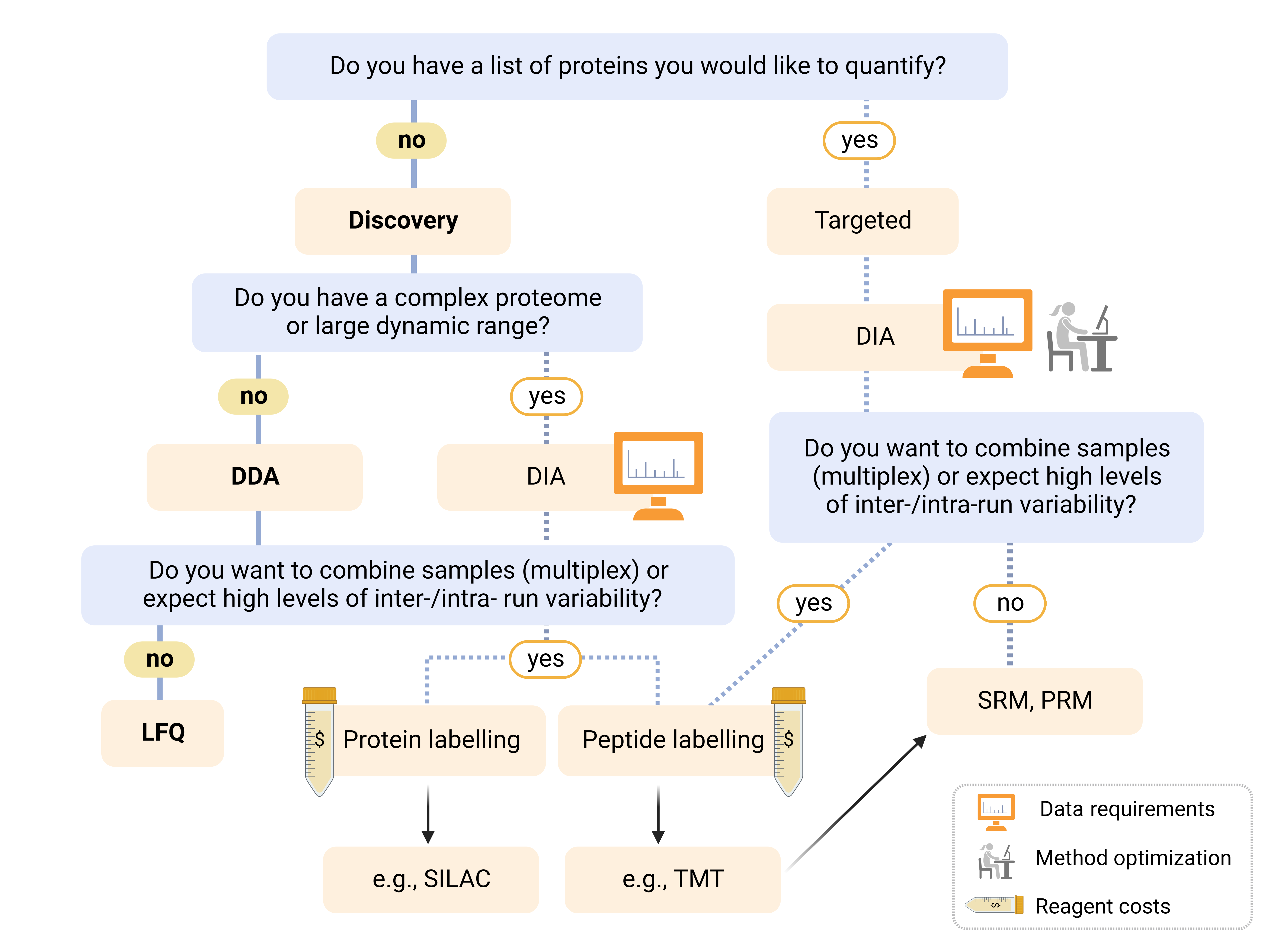 Discovery-based Quantitative MS methods
Discovery-based Quantitative MS methods
Quantitative Proteomics to Label or not to Label
Targeted Quantitative Proteomics MS Methods
MSF LFQ Service: Requirements and Deliverables