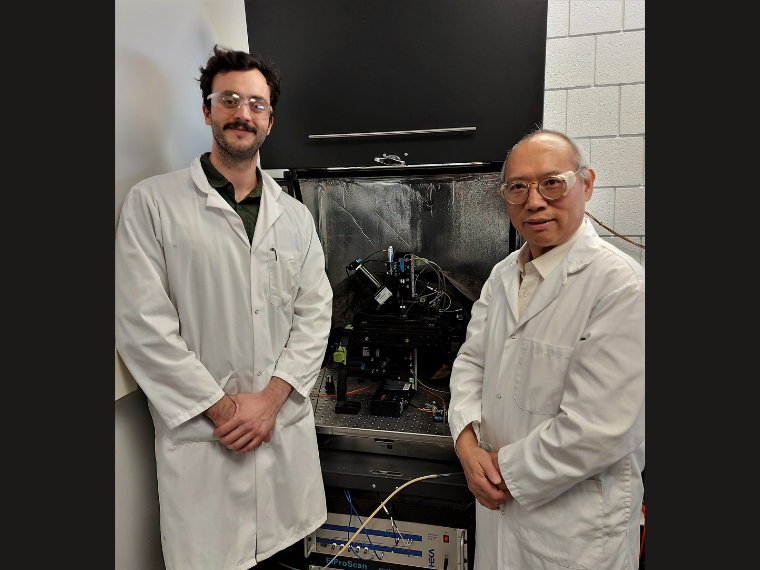
Catalysts' Edge: Powering Hydrogen From Water
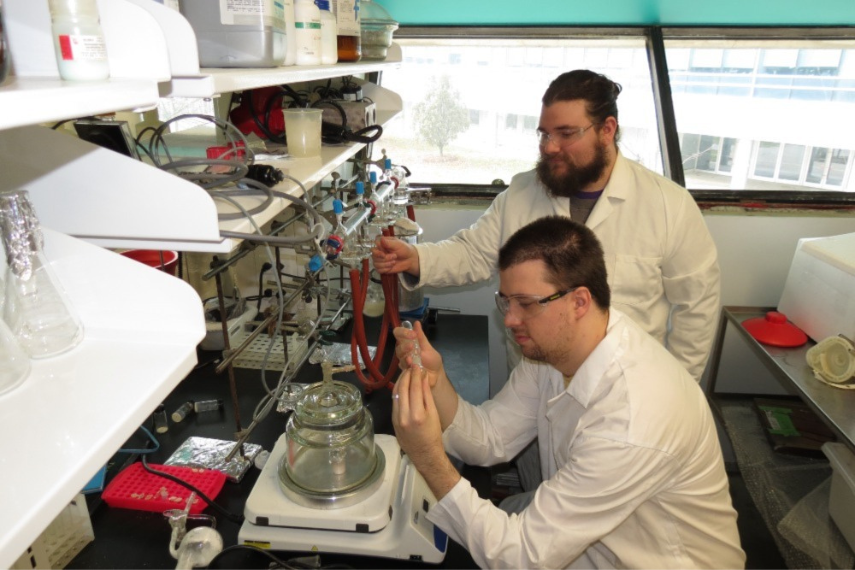
Exploiting catalysts' capabilities, Dr. Chen's team employs UV-Vis spectroscopy and SPECM to enhance water electrolysis efficiency for sustainable hydrogen fuel generation.
Water's Extraordinary Secret: Catalysts and Clean Energy